闭
竟然将近三个月没写推文,因为实在不知道有啥好写的...
每天除了上课以外也就是敲敲代码,画画画,看看动画,时间竟然也过得很快,一天、一个月转眼间就过去了。
最近呐,发现学过的东西一段时间不碰,很快就忘了。
但是忘了也没关系,学过的东西,捡回来也是很快的。
但是呐,要去哪里捡呢?这就得花不少时间和精力了。
为了避免这种事情发生,决定在捡回知识的同时找个地方把它存放起来,以后就好找了。
于是,我便开始拾取数据结构的碎片。
记得最开始是单链表,要知道无论是在内存(主存)还是在外存(硬盘)中,数据都是呈线性存放的。
在存储器里分成了很多小格子(以字节为单位),每个格子(字节)可以存放八位比特(bits),然后每个格子都有属于它自己的编号(即地址)。
在C语言中,声明一个指针变量(int *data),*data中存放的就是数据,data则指向的是地址。
那么为什么int最大值是2147483647呢?
int占4字节,即32位,最左边一位用来表示正负。
那么二进制最大值就是31个1,
转换成十进制就是2^32-1。
额,前面这些好像和单链表什么关系,扯远了,下面就是单链表正文。
以下内容使用Java实现
为什么需要单链表
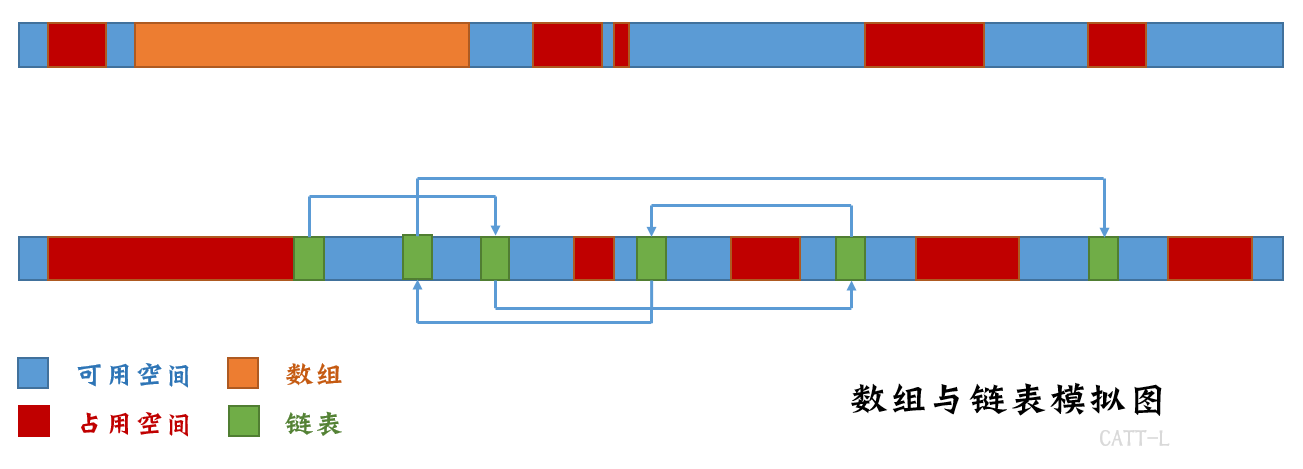
如果我们申请一个长度10000的整型数组,系统就会在内存中寻找长度为40kb的空间,这还是很好找的。
那如果长度为100万呢?或者更长呢?
也许就不是那么好找了,因为所需空间一定是要连续的,而内存中很可能没有那么多的连续空间。
因此我们需要一个链表,链表可以把每一个节点存储在内存的各个地方,在通过一根链把它们连接起来。
每个节点都只需要几字节的空间,那实在是太好分配啦。
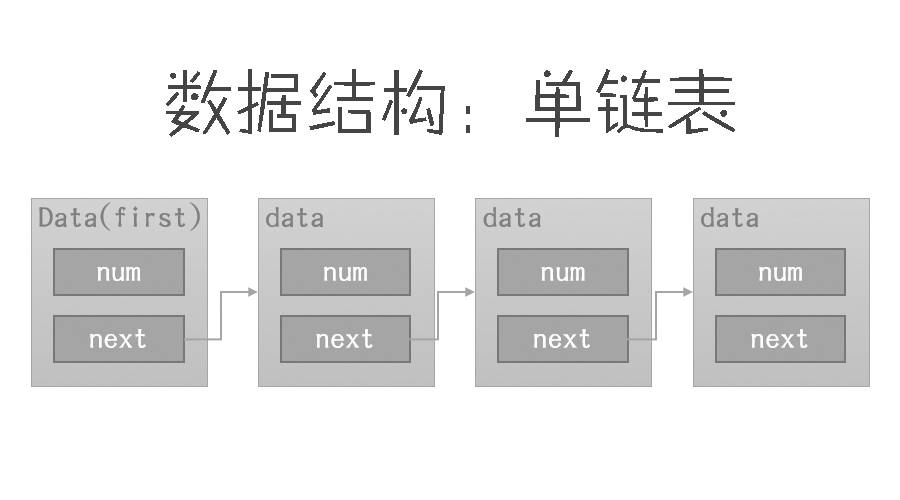
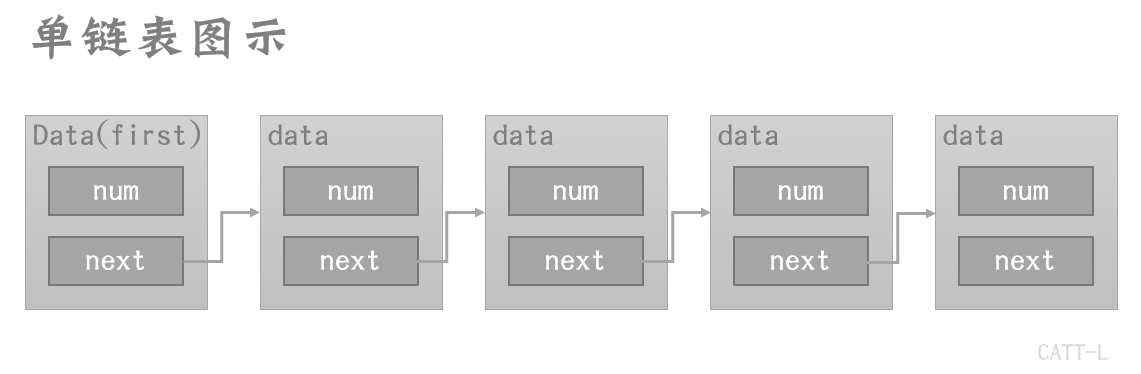
单链表的数据结构
单链表中的每一个节点,都分为两个区域,一个表示数据,另一区域指向下一节点。
怎么实现?
首先,国际惯例。
public class LinkedList{
public function static void main(String[] args){
}
}
在Java中,可以给节点创建一个类,并声明链表的头节点。
private class Data{
private int num; // 存放数据
private Data next = null; // 指向下一节点
Data(int num){
this.num = num; // 初始化类
}
}
// 头节点 不存放数据
private Data first = new Data(0);
给链表插入数据,有头插法和尾插法两种方式,头插法就是每次把数据放到第一位,尾插法就是把新数据放到末尾。
// 头插法插入节点
public void insertP(int num){
Data data = new Data(num); //创建子节点
data.next = first.next; //将子节点指向第一个节点
first.next = data; //将头节点指向子节点
}
// 尾插法插入节点
public void insertE(int num){
Data data = new Data(num);
Data cur = first;
while(cur.next != null){ //如果有后继结点,则判断下一个
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = data; //将末尾节点指向新的data节点
}
插入了数据,怎么把它们显示出来呢?
// 打印链表内容
public void display(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("链表为空");
Data cur = first.next;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.num + " " );
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
然后还有删除最前面的节点或最后面的节点
// 从头部删除节点
public void deleteP(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("删除头节点失败,链表为空");
else
first.next = first.next.next;
}
// 从尾部删除节点
public void deleteE(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("删除尾部节点失败,链表为空");
else {
Data cur = first;
//类似于尾插法
while(cur.next.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}
怎么删除指定的节点呢?
// 删除指定节点(所有符合要求的元素都删除)
public void remove(int num){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("链表为空");
else {
Data pre = first.next;
Data cur = pre.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = pre.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
}
}
}
}
// 删除指定节点(遇到的第一个)
public void removeOne(int num){
if(first.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
} else {
Data pre = first.next;
Data cur = pre.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
pre.next = cur.next;
// 和上面基本一样,但是删除之后就直接结束,不再往下判断。
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
查找结点
// 节点查找
public Object find(int num){
if(first.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return null;
} else {
Data cur =first.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
// 找到所需节点,将其返回
return cur.num;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(num + " 不存在\n");
return null;
}
}
然后测试一下吧~
public static void main(String[] args){
// 创建链表
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
System.out.println("前插法插入 1 2 3 4 5");
ll.insertP(1);
ll.insertP(2);
ll.insertP(3);
ll.insertP(4);
ll.insertP(5);
ll.display(); // 显示
System.out.println("删除头节点");
ll.deleteP();
ll.display();
System.out.println("尾插法插入 1 2 3 4 5");
ll.insertE(1);
ll.insertE(2);
ll.insertE(3);
ll.insertE(4);
ll.insertE(5);
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除尾节点");
ll.deleteE();
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除所有 1");
ll.remove(1);
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除第一个 3");
ll.removeOne(3);
ll.display();
System.out.println("查找 1");
if(ll.find(1)!=null) System.out.println(ll.find(1)+" 找到了\n");
System.out.println("查找 3");
if(ll.find(3)!=null) System.out.println(ll.find(3)+" 找到了\n");
}
测试结果如下
前插法插入 1 2 3 4 5 5 4 3 2 1
删除头节点 4 3 2 1
尾插法插入 1 2 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5
删除尾节点 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4
删除所有 1 4 3 2 2 3 4
删除第一个 3 4 2 2 3 4
查找 1 1 不存在
查找 3 3 找到了
到这里,单链表的基础功能就实现了~真是令人愉悦呢
这里是CATT-L,在现代魔法的道路中上下求索着。
以上 : )
完整代码
public class LinkedList {
private class Data{
private int num; //存放数据
private Data next = null; //指向下一节点
Data(int num){
this.num = num; //初始化类
}
}
private Data first = new Data(0); //头节点 不存放数据
// 头插法插入节点
public void insertP(int num){
Data data = new Data(num); //创建子节点
data.next = first.next; //将子节点指向第一个节点
first.next = data; //将头节点指向子节点
}
// 尾插法插入节点
public void insertE(int num){
Data data = new Data(num);
Data cur = first;
while(cur.next != null){ //如果有后继结点,则判断下一个
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = data; //将末尾节点指向新的data节点
}
// 从头部删除节点
public void deleteP(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("删除头节点失败,链表为空");
else
first.next = first.next.next;
}
// 从尾部删除节点
public void deleteE(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("删除尾部节点失败,链表为空");
else {
Data cur = first;
//类似于尾插法
while(cur.next.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
}
}
// 节点查找
public Object find(int num){
if(first.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return null;
} else {
Data cur =first.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
// 找到所需节点,将其返回
return cur.num;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println(num + " 不存在\n");
return null;
}
}
// 删除指定节点(所有符合要求的元素都删除)
public void remove(int num){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("链表为空");
else {
Data pre = first.next;
Data cur = pre.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = pre.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
cur = pre.next;
}
}
}
}
// 删除指定节点(遇到的第一个)
public void removeOne(int num){
if(first.next == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
} else {
Data pre = first.next;
Data cur = pre.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.num == num){
pre.next = cur.next;
// 和上面基本一样,但是删除之后就直接结束,不再往下判断。
return;
}
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
// 打印链表内容
public void display(){
if(first.next == null)
System.out.println("链表为空");
Data cur = first.next;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.num + " " );
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
// 创建链表
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
System.out.println("前插法插入 1 2 3 4 5");
ll.insertP(1);
ll.insertP(2);
ll.insertP(3);
ll.insertP(4);
ll.insertP(5);
ll.display(); // 显示
System.out.println("删除头节点");
ll.deleteP();
ll.display();
System.out.println("尾插法插入 1 2 3 4 5");
ll.insertE(1);
ll.insertE(2);
ll.insertE(3);
ll.insertE(4);
ll.insertE(5);
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除尾节点");
ll.deleteE();
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除所有 1");
ll.remove(1);
ll.display();
System.out.println("删除第一个 3");
ll.removeOne(3);
ll.display();
System.out.println("查找 1");
if(ll.find(1)!=null) System.out.println(ll.find(1)+" 找到了\n");
System.out.println("查找 3");
if(ll.find(3)!=null) System.out.println(ll.find(3)+" 找到了\n");
}
}